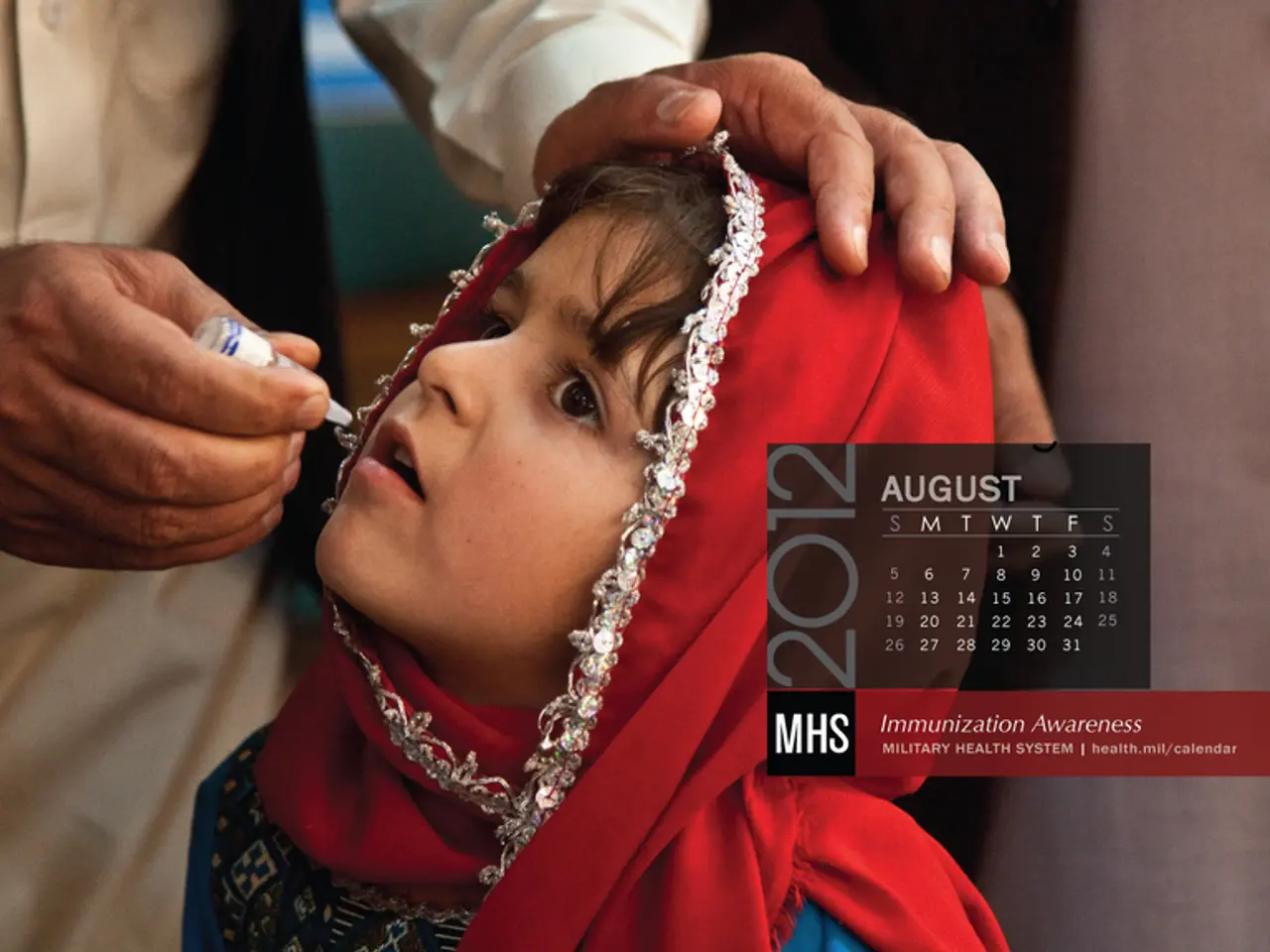
Pharmaceutical giant, Pfizer, takes action by deploying its Mexican manufacturing hub to counteract the local drop in vaccination rates.
In a move that could significantly impact the Mexican pharmaceutical landscape, global pharmaceutical giant Pfizer is reportedly increasing its investment in Mexico, particularly in clinical research and vaccine production.
The Toluca plant, Pfizer's key vaccine supplier in Latin America, employs 420 people and has an annual manufacturing capacity of 194 million units. The facility, which labels, stores, and distributes products to 10 Latin American countries and regions, is also involved in Pfizer's campaign to promote its 20-valent pneumococcal vaccine, a more effective version that protects against seven more pneumococcal infections than the previous 13-valent version.
Mexico's pharmaceutical sector, particularly its Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) market, is poised for significant growth. With projected expansion from US$4.39 billion in 2024 to US$7.42 billion in 2033, the market reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.02%. Key drivers include increasing demand for generic medicines and treatment for chronic diseases, enhanced domestic manufacturing capacity, and government policies aimed at reducing reliance on imported APIs and promoting local production.
Pfizer's increased investment in Mexico aligns with its broader goals to strengthen manufacturing and supply chain resilience, expand clinical research capacity, leverage government incentives, and address unmet medical needs. By diversifying its manufacturing and supply chains, Pfizer aims to reduce dependency on any single region, crucial in a post-pandemic, geopolitically complex world. Strengthening its local presence could facilitate faster regulatory approvals, improved patient recruitment for trials, and better market penetration.
For Mexico, increased foreign direct investment could boost local manufacturing, create skilled jobs, and enhance technological transfer. Expanded clinical research and vaccine production capacity could improve access to innovative medicines and vaccines, addressing both communicable and non-communicable diseases. Closer ties with multinational corporations like Pfizer could elevate Mexico’s profile in global pharmaceutical innovation and supply chains.
However, vaccination rates in young children in Mexico have dipped to around 78 or 80%, compared to 95% a few years ago. This decline can be attributed to a global shortage of vaccines and misinformation. Dr. César Martínez Longoria, a specialist in pediatrics and pediatric infectious disease, partially blames the decline in vaccination rates on parents not understanding the importance of vaccinating their children.
Diana Cruz Salazar, the manufacturing site leader of the Pfizer Toluca Manufacturing Plant, expressed concern about the decline in vaccination rates and the importance of reaching every person to prevent diseases that constantly threaten. She stated that Pfizer is interested in promoting vaccination not only in Mexico but worldwide.
Pfizer's pneumococcus vaccine is manufactured in Ireland before being shipped to its Toluca plant for labelling and packaging. The New York-based pharmaceutical company invests between US $12 million and $15 million in its Toluca plant annually. In January, Pfizer Mexico announced plans to increase its investment in Mexico, particularly in clinical research.
As Pfizer increases its investment in Mexico, it is expected to contribute to accelerated local industry growth, improved healthcare access, and greater integration into global pharmaceutical value chains. Pfizer, on the other hand, would gain strategic diversification, cost advantages, and enhanced market access.
Science news: Pfizer's increased investment in Mexico, particularly in clinical research and vaccine production, could lead to improved health-and-wellness outcomes in the region by enhancing access to innovative medicines and vaccines, addressing both communicable and non-communicable diseases.
In line with Pfizer's broader goals to address unmet medical needs, strengthen manufacturing and supply chain resilience, and promote health-and-wellness, the company's expansion in Mexico is expected to help in the global campaign to promote its 20-valent pneumococcal vaccine, which offers greater protection against pneumococcal infections.